Today’s News

Image Source: Euronews Business
On Tuesday, the World Bank warned that the world economy could experience a “wasted” decade and its weakest growth in 30 years. It foresees a year marked by sluggish growth, pointed to a slow recovery from the pandemic and ongoing wars in Ukraine and the Middle East as major factors expected to heavily impact economic progress.
In its semiannual Global Economic Prospects report, the World Bank projects a further slowdown in 2024, with global output expected to diminish from 2.6 percent to 2.4 percent. Despite some resilience, the report emphasizes elevated uncertainty due to ongoing conflicts, a shrinking Chinese economy, and escalating risks associated with climate change-induced disasters.
The convergence of crises in recent years has brought forth the potential for the weakest half-decade economically in the last 30 years. Indermit Gill, Chief Economist of the World Bank Group remarked on this by saying, “Without a major course correction, the 2020s will go down as a decade of wasted opportunity”.
Global growth appears on track to decline for the third consecutive year, especially impacting developing nations grappling with high borrowing costs and stagnant trade volumes.
The report highlights potential repercussions of conflicts, particularly the Middle East tensions between Israel and Hamas. Geopolitical risks loom large, with fears that heightened conflict could propel energy prices skyward, causing global ramifications on economic activity and inflation. Recent military activities in the Red Sea have already influenced oil prices and freight and insurance rates, affecting maritime traffic.
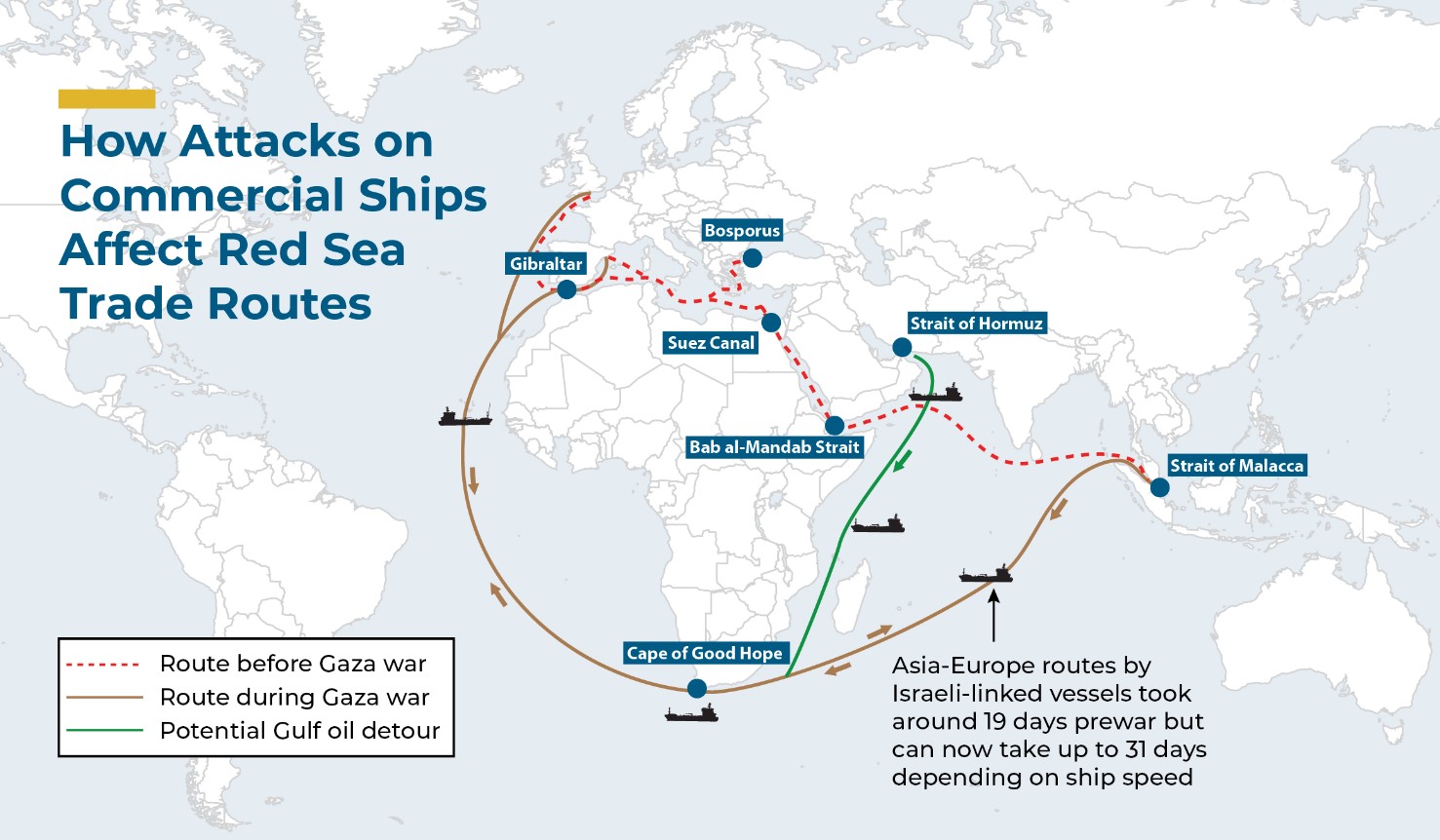
Image Source: The Washington Institute
According to economists at Capital Economics in their recent report, the re-routing of trade ships from the Red Sea isn’t likely to cause a sudden return of worldwide inflation. However, they cautioned that if the conflict broadens into a regional scale, it might bring about inflationary dangers.
The disturbances in shipping routes come after a year where global trade growth experienced its slowest pace in the last 50 years, excluding periods of global recessions, as per the World Bank.
The World Bank anticipates that if the Middle East conflict doesn’t escalate further, global oil prices will slightly decrease this year. This expectation arises from the predicted weakening of growth and an increase in oil production
Despite a sluggish recovery, concerns persist over the fragility of China’s economy, especially evident in the property sector and subdued consumer spending, potentially affecting Asia’s trading partners. China is forecasted to experience its slowest growth outside pandemic downturns in three decades, with growth anticipated to drop from 5.2 percent in 2023 to 4.5 percent in the current year.
Europe and the United States are poised for another year of feeble economic output in 2024. Economic growth in the Eurozone is expected to slightly improve from 0.4 percent to 0.7 percent. Conversely, in the U.S., growth is anticipated to slow from 2.5 percent in 2023 to 1.6 percent in the current year due to high-interest rates and reduced government spending, leading businesses to adopt a cautious investment approach amid economic and political uncertainty, including the upcoming 2024 election.
Despite these challenges, Biden administration officials remain optimistic, asserting their success in managing inflation while sustaining a robust labor market, framing it as a “soft landing.” Treasury Secretary Janet L. Yellen expressed satisfaction with the decline in inflation despite strong labor market conditions.
Other News
ESG Fund Launches Decline Amid Regulatory Pressure
ESG fund launches plummet as regulatory scrutiny increases, with only six new funds in the second half of 2023 and managers removing ESG labels amidst mounting pressures.
BlackRock Plans Job Cuts To Bolster Growth
BlackRock is trimming 600 jobs, 3% of its staff, to boost focus on tech, ETFs, and private markets. CEOs aim to expand their workforce by 2024, stressing agility and tech for client needs and growth opportunities.
Intel Agrees To Buy Silicon Mobility SAS
Intel has acquired Silicon Mobility SAS, specializing in electric vehicle technology and AI integration, as part of its CES announcement to penetrate the automotive sector.



